Ready to use legal template
Drafted by experienced lawyers
Compliant with Indian law
Ready to use legal template
Drafted by lawyers
Compliant with Indian law
Learn more about Employment Termination Letter in India
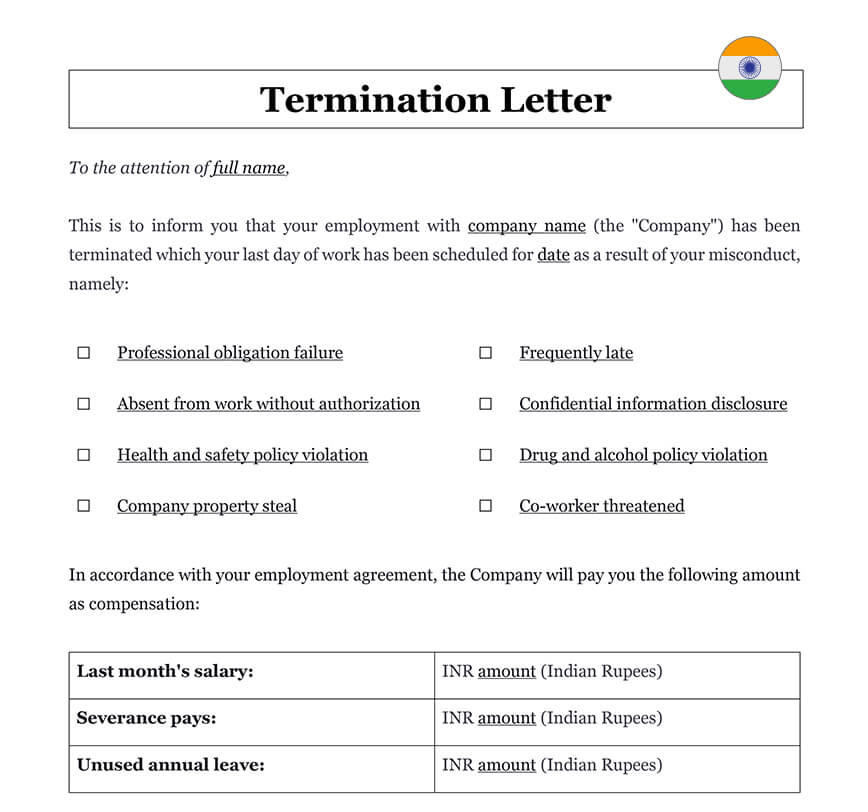
An Employment Termination Letter is a formal document issued by an employer to notify an employee of the end of their employment. This letter outlines the reason for termination, the effective date, and any other pertinent details related to the employee’s departure, including final compensation or benefits. In India, it is essential for this letter to be clear, concise, and legally compliant, as it helps avoid potential disputes or misunderstandings regarding the termination process. Our Employment Termination Letter, expertly drafted to comply with Indian labor laws, provides a comprehensive framework for employers to manage the termination process smoothly and professionally. You can download the Employment Termination Letter in Word format and customize it as needed for your specific circumstances in India.
Table of contents
-
What is an Employee Termination Letter in India?
-
What are the rules governing Employee Termination Letter in India?
-
How to terminate an employee in India?
-
How to comply with the law when terminating an employee?
-
Do you need to send termination notice?
-
Do you have to pay any compensation?
-
What to do against wrong termination?
What is an Employee Termination Letter in India?
An Employee termination letter in India is used when an employer needs to terminate an employee’s employment for something they have done. Often, Employee termination letters in India are sent after an employer notice that an employee has engaged in behavior that is not acceptable or not allowed.
It is common in situations that require an Employee termination letter to speak to the employee about the behavior or performance in person, either immediately before or immediately after the letter is sent, but it is not required. A formal record should be created of the employee’s poor behavior or performance before termination.
What are the rules governing employee termination letter in India?
Firstly, any termination must comply with federal and state laws, as these laws supersede contractual provisions. Thus, contractual provisions must be consistent with the law. State laws are particularly important where there are no defined termination procedures or where there is a dispute in the interpretation of those procedures.
Secondly, it is relevant to examine the laws governing termination in several destinations in India. These case analyses represent standards in state labor laws across India:
| ➤ The Union Territory of Delhi State labor law: Under the Delhi Shops and Establishments Act, 1954, an employer may not terminate an employee who has worked for the company for more than three months without giving the employee at least 30 days' notice or pay instead of notice. The employer is not required to give notice if misconduct is the cause of the termination. However, the employee in such circumstances should be given a reasonable opportunity to explain the charge against him or her before termination. |
| ➤ Maharashtra State Labor Law: Under the Maharashtra Shops and Establishments Act, 1948, an employer may not dismiss an employee who has been with the company for more than one year without giving the employee at least 30 days written notice. If an employee has been with the company for more than three months but less than one year, the employer must give at least 14 days' notice. Notice is not required if the employee is terminated for misconduct. |
| ➤ Karnataka and Tamil Nadu State labor laws: Under the Karnataka Shops and Establishments Act, 1961 and the Tamil Nadu Shops and Establishments Act, 1947, an employer may not dismiss an employee who has been with the company for more than six months, except for "reasonable cause”. In addition, an employer must provide one month's notice. If misconduct is the termination’s cause, no notice or associated payment is required. |